Denmark’s educational system
Share your new idea with us today
And leave the beginning of your education to us.
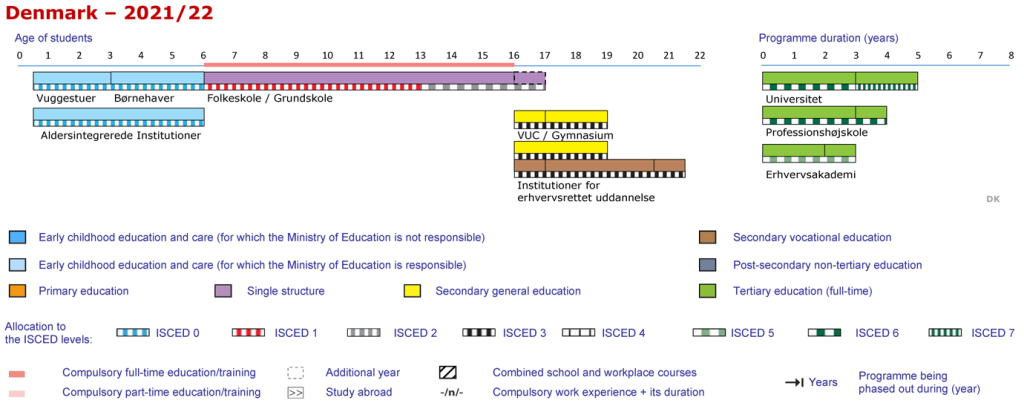
Primary education in Denmark consists of a combination of primary and lower secondary education. Primary and lower secondary schools are educational facilities where primary and lower secondary education is provided (in Danish: Folkeskole). Between the ages of six and sixteen, primary education is required and consists of one pre-school year (grade 0) and nine school years (grades 1-9). A tenth grade can be added to the required schooling; however, it is an optional extra.
Students have the freedom to pick their educational path after completing primary and lower secondary education. In a nutshell, academically oriented general upper secondary education programs and secondary vocational education programs are the options.
General upper secondary education programmes take place at several institutions whereas some institutions offer various types of programmes:
- The three-year upper secondary school leaving examination (STX) takes place at upper secondary schools (in Danish: gymnasium)
- The three-year higher commercial examination (HHX) takes place at commercial upper secondary schools, also known as business colleges (in Danish: handelsgymnasium)
- The three year higher technical examination (HTX) takes place at technical upper secondary schools, also known as technical colleges (in Danish: teknisk gymnasium)
- The two-year higher preparatory examination (HF) usually takes place at upper secondary schools (in Danish: gymnasium), but the programme is also offered at adult education centres (VUC Centres).
The three first-mentioned programs each have a three-year lifespan. Students typically begin at the age of 16 and complete their education at the age of 19. This, however, is contingent on several criteria, including whether the kid in issue has completed the tenth grade. The last of these, HF, is a two-year program with a wide range of ages among the students.
The length of secondary vocational education programs varies based on the program. The lifespan spans from 112 to 512 years, with the most common being 312 to 4 years. The courses are taught at vocational and technical schools (in Danish: erhvervsskole). The age of students when they begin and when they graduate varies significantly.
There is a wide range of educational alternatives for students following general upper secondary school programs and secondary vocational education programs. In general, regular upper secondary education prepares students for further education, whereas secondary vocational education prepares students for employment.
Higher education takes place at different educational institutions:
- Short-cycle programmes are offered at business academies (in Danish: erhvervsakademi)
- Medium-cycle programmes are offered at university colleges (in Danish: professionshøjskole)
- Long-cycle programmes are offered at universities (in Danish: universitet)
